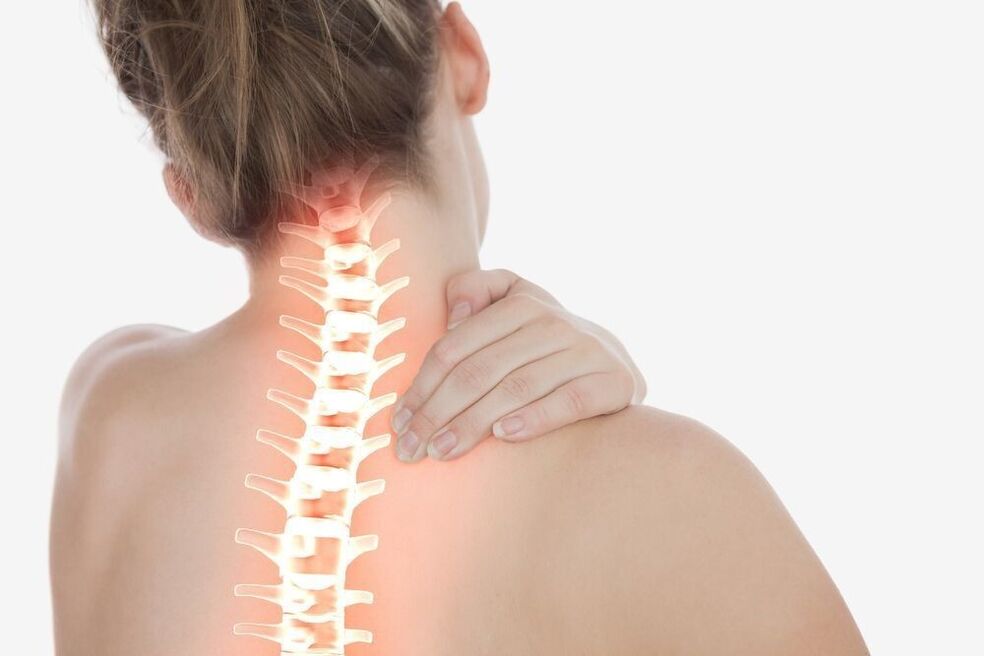
The spine, like any structure that has a support function, inevitably wears out over time. High static and dynamic loads and local overloading of the segments of the particularly mobile upper part lead to a decrease in the ability to regenerate and a gradual degeneration of the cartilaginous and adjacent muscular-ligamentous structures. By the age of 30-35, almost everyone shows more or less signs of cervical osteochondrosis. And while it is impossible to stop the irreversible process of biological aging, it is entirely possible to slow it down.
diagnosis
Methods of radiological imaging are used for the objective assessment of the condition and for the detection of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the cervical spine:
- simple spondylography (X-ray examination without contrast agent in frontal, lateral and oblique projections)
- X-ray image with functional tests
- MSCT (multi-slice computed tomography)
- MRI
- Survey spondylography of the upper spine is a traditional method of radiological diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis. With its help, the condition of the vertebral bodies is assessed, their shape, height, degree of deformation and displacement relative to one another are determined. Osteophytes, areas of enlightenment in focal points of the liquefaction of bone tissue, are made visible on x-ray images.
- Functional spondylography is a study that aims to identify signs of movement disorders. The x-ray is performed with a firm maximum flexion and extension of the cervical spine.
- MSCT is an advanced alternative to x-rays. Bone structures, intervertebral discs, ligamentous apparatus, spinal canal and spinal cord are visualized in more detail on multi-layer images.
- Magnetic resonance imaging enables additional visualization of the cartilage layer and other soft tissues of the vertebral joints. The study is prescribed for severe neurological symptoms to distinguish cervical osteochondrosis from acute intervertebral hernia.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is aimed at eliminating pain and slowing the progression of the pathological process. It is carried out in two directions: limiting the effects of adverse factors and suppressing the mechanisms of disease development.
The therapeutic and prophylactic measures that minimize the effects of pathogens include:
- rational selection of work furniture
- Use of orthopedic mattresses and pillows
- Correction of hearing, eyesight and posture
- Carrying special fasteners
- Restriction of work activity combined with a longer stay in a forced situation
- adequate physical activity
- right nutrition
There are many different methods of therapeutic correction aimed at slowing down the development of the degenerative process.
Massage for cervical osteochondrosis
Massage procedures for relieving inflammation and eliminating pain are part of the complex of mandatory therapeutic measures. The most effective types of neck massage:
- classic
- medical (manual)
- Point (acupuncture)
- Vacuum (cans)
- hardware
Thanks to massage techniques, the local blood and lymph circulation is improved, tissue trophy accelerates, muscle tension is eliminated, tension in the neck is released, and muscle tone and elasticity are improved.
Orthopedic collars
Special orthopedic aids (shants collars) are used to fix the cervical spine in the correct position. Removable structures of different sizes, shapes and rigidity limit the usual pathological head posture, control movements in the neck, reduce pressure on the spinal segments, warm and relax tense muscles and prevent further progression of the disease.
The neck brace for osteochondrosis is available in several modifications:
Soft rails made of medical foamor other porous hypoallergenic materials have a notch for the chin and lower surfaces of the neck and mounts. They are used to correct minor diseases of the upper spine, the anatomically correct posture of the vertebrae and the relaxation of the shoulder girdle muscles.
Pneumatic (inflatable) collarsare designed to prevent pain, pull smoothly, and eliminate compression of the vertebral artery.
Semi-rigid bandagesequipped with metal inserts reliably stabilize the intervertebral segments. They significantly limit the range of motion and contribute to widening the gaps between the vertebral bodies.
Rigid corsets made of durable plasticdesigned to completely immobilize the cervical spine in a neutral position. Prescribed in the late stages of the disease, accompanied by compression disorders.
The collar for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is selected by the doctor taking into account the age, anatomical features and the stage of the degenerative process.
Manual therapy
Manual therapy aims to identify and remove blockages in the motor segments. A locally dosed action on the vertebral joints helps normalize blood flow and supply to the brain, relieve compression (entrapment) and restore normal function of nerve fibers. Targeted manipulations by the chiropractor will allow you to achieve maximum relaxation, get rid of muscle spasms, cervicogenic headaches due to damage to the anatomical structures of the neck and tension headaches.
acupuncture
Acupuncture, in which acupuncture needles are inserted into bioactive points in the neck and shoulder blades, focuses on restoring the disturbed energy balance. By stimulating the rapid contractions of sensitive nerve fibers and releasing endorphins and neurotransmitters, acupuncture has powerful anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects on cervical osteochondrosis. Thanks to this technique, numbness in the hands, dizziness, tinnitus, improves blood circulation and optimizes mobility.
physical therapy
Physiotherapy of degenerative diseases of the spine aims to relieve pain and stimulate recovery processes. The greatest therapeutic effect is achieved through:
- UFO
- Ultrasound treatment
FAQ
How to get help with acute pain with osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine?
If acute pain occurs suddenly, the lower back must be restrained. This immobilizes spasmodic muscles and shifts the load off them. Then, if possible, lie the patient on their back with a pillow under their bent knees. To relieve pain, you should take a drug with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects (NSAID). In addition, you can use an ointment or gel based on diclofenac or its analogues, or apply a cold compress (no more than 10 minutes). It is very important to get rid of the load on the spine and see a doctor as soon as possible.
Is it possible to do physical exercises with lumbar osteochondrosis?
Physical education in lumbar osteochondrosis is not only not prohibited, but also recommended (with the exception of an acute phase of pain). However, you should be careful not to allow any axial load on the spine and categorically refuse to squat, jump, and lift weights. The exercise set should be selected individually by a specialist.




























